Understanding Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (ADS-B): A Foundational Technology in Modern Aviation
In the sphere of modern aviation, precision, safety, and efficiency are paramount. A cornerstone technology enabling advancements in these areas is Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast, commonly known as ADS-B.
Defining ADS-B: A Technical Overview
ADS-B is an advanced surveillance technology that allows aircraft to automatically transmit flight information without pilot or controller intervention. The acronym itself provides a concise summary of its function:
- Automatic: The system operates autonomously, requiring no manual input from the flight crew for its primary surveillance function.
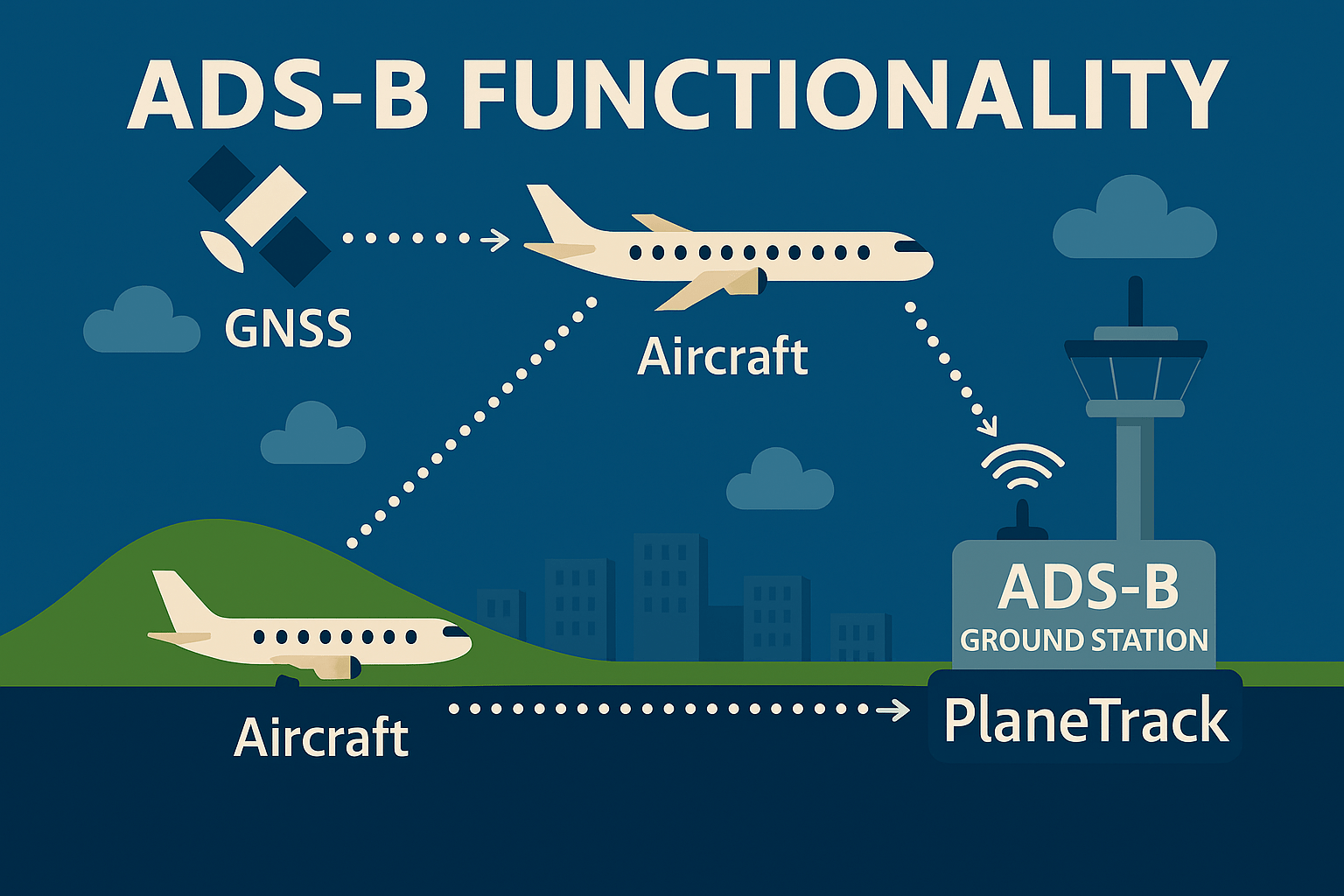
- Dependent: The accuracy of the broadcast data relies on the aircraft’s own navigation systems, principally the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), such as GPS, to determine its precise position.
- Surveillance: It provides a method of observing and tracking aircraft, replacing or augmenting traditional radar systems.
- Broadcast: Aircraft periodically transmit their data (including identity, GNSS-derived position, altitude, velocity, and other parameters) to any suitably equipped receivers.
This broadcast information is accessible to Air Traffic Control (ATC) ground infrastructure, and dedicated ADS-B receiving units, industrial and defense ground stations and other interested users.
Operational Mechanics of ADS-B
Aircraft equipped with an “ADS-B Out” transponder utilize their onboard GNSS receiver to ascertain their precise geographical coordinates. This positional data, along with other vital flight parameters, is then typically broadcast once per second via a digital data link, commonly on the 1090 MHz frequency (known as 1090ES or 1090 MHz Extended Squitter).
The system comprises two main components:
- ADS-B Out: This refers to the aircraft’s capability to transmit its state vector (position, velocity, etc.) and other information. Regulatory bodies worldwide have increasingly mandated ADS-B Out equipage for aircraft operating within designated airspaces, recognizing its significant contribution to air traffic visibility and accuracy.
- ADS-B In: This is the complementary capability to receive ADS-B data transmitted by other aircraft. For pilots, ADS-B In provides enhanced situational awareness through cockpit displays of traffic information (CDTI). It can also deliver Flight Information Services-Broadcast (FIS-B) – such as weather products – and Traffic Information Services-Broadcast (TIS-B), which rebroadcasts radar data for non-ADS-B equipped aircraft.
The Significance of ADS-B in Aviation
The implementation and adoption of ADS-B technology deliver substantial benefits across the aviation spectrum:
- Improved Situational Awareness: Both flight crews and air traffic controllers benefit from a more comprehensive and real-time depiction of the air traffic environment.
- Extended Surveillance Coverage: ADS-B facilitates surveillance in regions where traditional radar deployment is impractical or cost-prohibitive, including oceanic, mountainous, and remote terrestrial areas.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The ground infrastructure for ADS-B can be less expensive to install and maintain compared to primary and secondary surveillance radar systems.
- Data Accessibility: Beyond operational ATC use, ADS-B data is accessible to airlines for operational monitoring and other interested parties via special ground stations.
As a provider of ADS-B receiving solutions, we recognize the advanced role this technology plays. Our devices empower users to connect directly with this stream of aviation data, offering unique insights into the complex and dynamic nature of air traffic.
We encourage you to explore our range of ADS-B receivers and delve deeper into the capabilities this transformative technology offers.
Our products for ADS-B
-
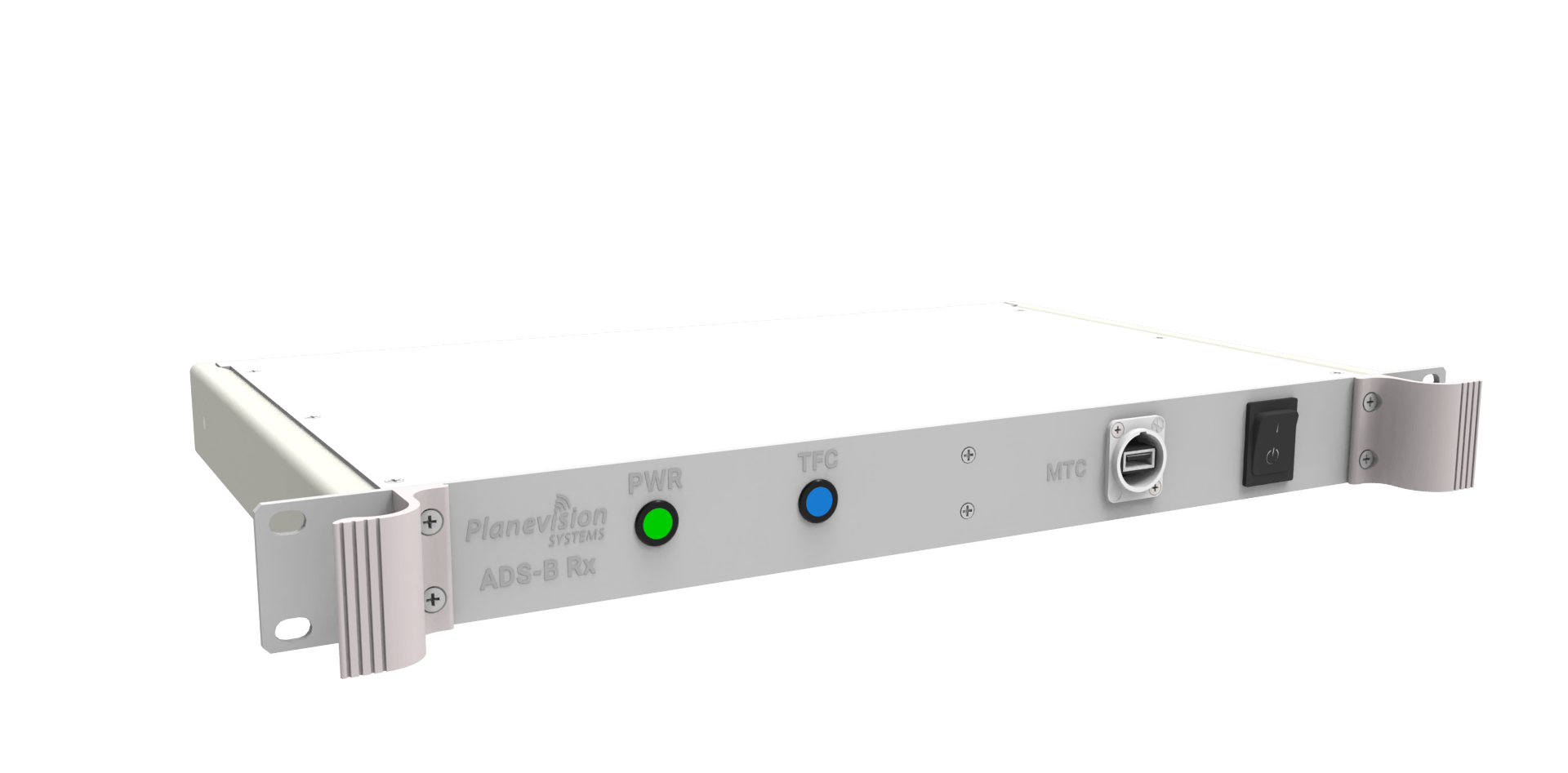
PlaneTRack B10
PlaneTRack Type B10 is a cost-efficient, professional 2U 10-inch ADS-B ground station tailored for monitoring ADS-B-equipped aircraft.
-
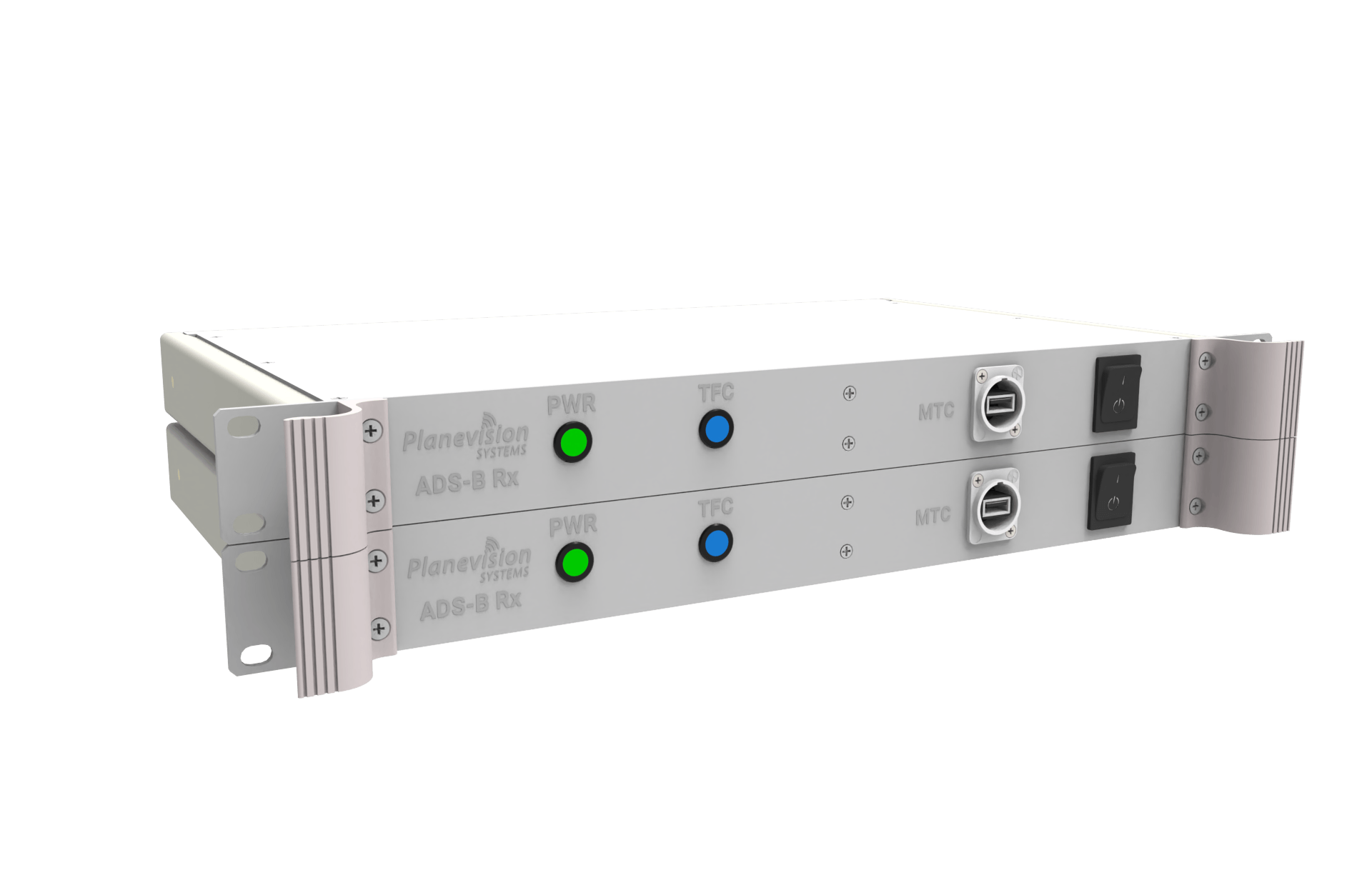
PlaneTRack RDM1U
PlaneTRack Type RDM is the ideal solution for receiver sites that require full redundancy or dual antennas that are required due to partially obstructed views.
-
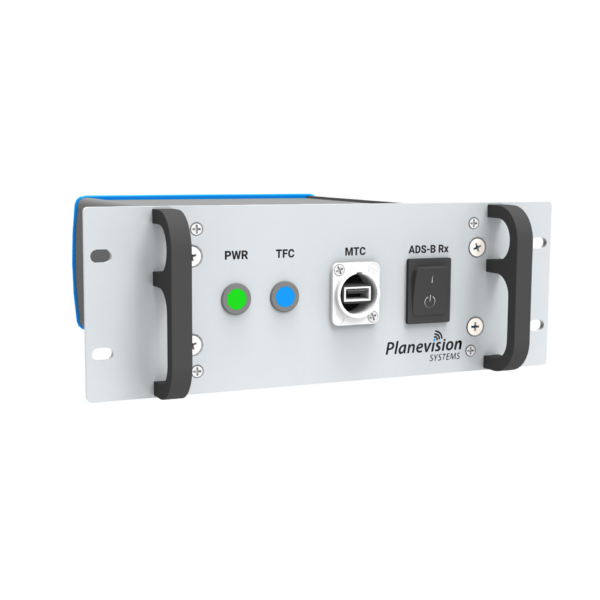
PlaneTRack B1U
PlaneTRack Type B1U is a cost-efficient, professional 1U 19-inch ADS-B ground station tailored for monitoring ADS-B-equipped aircraft.
-
PlaneTRack BDM
PlaneTRack Type BDM is the ideal solution for dual power receiver sites that require 19″ plug-n-play rack inserts.
-
PlaneTRack B
PlaneTRack Type B is a cost-efficient, professional 2U 19-inch ADS-B ground station tailored for monitoring ADS-B-equipped aircraft.